Category G: Engagement
Influencing governments and policymakers, and stakeholder engagement (5% of total score)
This Category consists of two equally weighted criteria:
-
G1
Engaging and influencing governments and policymakers
-
G2
Stakeholder engagement and partnerships
To perform well in this Category, companies should:
- Commit to engage with the Indian government and policymakers in support of preventing and addressing obesity, diet-related chronic diseases, undernutrition and micronutrient deficiencies; and show evidence of support and actions taken.
- Disclose their positions on nutrition issues in India and ensure transparency around their membership and funding of industry associations, think-tanks, etc., and highlight potential conflicts of interest or present commentary on influencing activities.
- Demonstrate a comprehensive, structured approach to stakeholder engagement.
- Provide evidence of extensive engagement with stakeholders and/or evidence of partnerships with expert organizations to solicit input on their nutrition strategies, policies and practices.
- Publish reports on how the input received through stakeholder engagement is used to improve the company’s nutrition strategies, policies and/or practices.
Context
Companies’ interactions with respect to directly influencing public and government policies is not legally regulated in India. However, there are opportunities and channels for local and international food and beverage companies to engage with the Indian government and other policymaking bodies at various levels to support the national nutrition mission and help address India’s most pressing nutrition challenges. These challenges remain a serious threat for the country to reach its full potential as shown by the results from the first phase of the fifth and the latest round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5), conducted in 2019-2020. The data indicate a decline in nutritional status of children under 5 years, and anemia among women remains a major cause of concern. Obesity among adults is increasing. Companies for instance, can provide support through interest and advocacy groups (or individuals), the internal public affairs division, industry associations, think-tanks, etc. with whose help companies can facilitate and maintain their interactions with the government. In addition, companies can support and positively engage with regulatory bodies such as the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), the apex government body mandating food regulations, on all issues concerning food and beverage manufacturers.
In recent years, FSSAI has strengthened the regulatory environment and encouraged and supported improved compliance of companies with its regulations. For example, in December 2017, FSSAI established a self-regulation platform, the Responsible Food Companies Score for food companies, retailers stocking packaged food, and fast-food restaurant chains.
At the same time, FSSAI withdrew all old cases of non-compliance against food business operators, including food manufacturers that were deemed redundant to its revised standards. Since then, engagement between the food regulator and major food companies has led to improved dialogues. Food and beverage companies therefore have a crucial role to play in voicing their support towards policy efforts that improve public nutrition.
Effective stakeholder engagement and partnerships are also vital to integrate food and beverage companies’ work in order to have an impact on the wider-nutrition agenda in India. According to a report published by Global Corporate Governance Forum, poor stakeholder engagement has business and reputational risk. In contrast, a long-term, strategic approach that consists of a clear objective, thorough consultations, a focused-plan and greater understanding of stakeholder needs and priorities, can support sound business results, innovation and better nutrition. In this regard, national governmental and non-governmental organizations, such as the National Institute Nutrition, Tata Trusts (specially, with their India Nutrition Initiative), as well as other national/international institutions, such as Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN), United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP), Save the Children, etc., are some of the key organizations working on nutrition issues in India. Companies can solicit input from them to guide their commercial nutrition strategy and practices.
How do food and beverage companies engage with government and policymakers, and other stakeholders amidst the COVID-19 crisis?
- Food and beverage companies assessed in this Index can support government actions and efforts to assist the most vulnerable sections of society during the COVID-19 pandemic and improve access to food. Mother Dairy, for instance, made special arrangements to place its kiosks or small retail outlets that enable supply of milk and milk products at specific declared hotspots, and worked with local administrators to overcome supply challenges.
- Companies can also collaborate with international organizations, academic experts and/or NGOs to inform their nutrition-sensitive strategies and interventions. For instance, Hindustan Unilever worked with UNICEF to raise awareness about COVID-19 among tea-plantation workers and local communities in Assam State, including provision of hygiene products. PepsiCo India’s website highlights that it has partnered with foundations and local authorities to distribute cooked meals and dry food to over 8,000 vulnerable families.
• In addition, companies could harness the collective power of the food and beverage industry by leading or joining industry-wide initiatives to address COVID-19-related nutrition challenges. For instance, companies were seen engaging through the support of trade associations, such as the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), the US India Strategic Partnership Forum and the All-India Foods Processors’ Association, to gain ‘essential service’ status in order to maintain uninterrupted food supply to Indian consumers when the initial lockdown in March 2020 was announced and there were persisting ambiguities surrounding the lockdown restrictions for large food and beverage companies.
The India Spotlight Index 2020 research did not include indicators to score and rank companies’ responses to the COVID-19. But ATNI did talk to companies about their initial coping strategies and responses to the pandemic between March and June 2020 and ATNI has been tracking publicly available information on industry’s response globally to the COVID-19 crisis, including in India, and reported on trends, best practices and areas of concern in separate reports. Read more about how companies can positively contribute to addressing the global nutrition challenges in ATNI’s COVID-19 Project.
ATNI Covid-19 ProjectMain messages
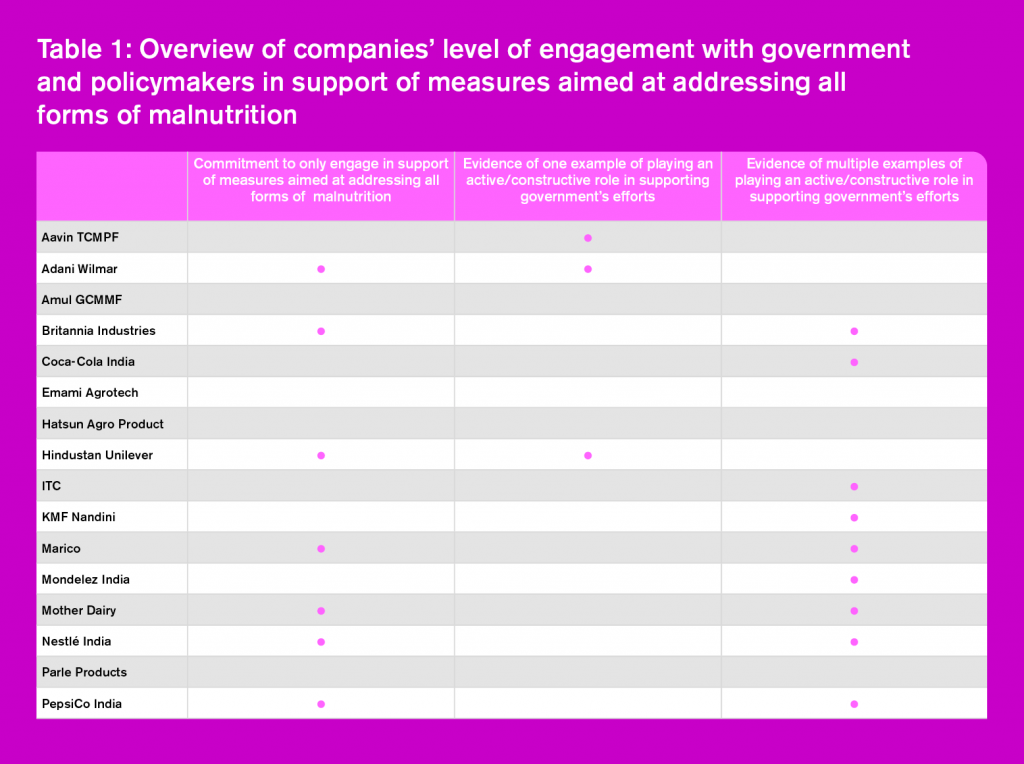
- Nestlé India achieves the highest score of 6.8 out of 10 for its overall performance in engagement with government and policymakers and other relevant stakeholders impacting nutrition-related activities and initiatives in India, similar to 2016. The company shows a comprehensive level of engagement with internal and external stakeholders to improve its commercial nutrition strategy, and to support the development of public strategies aimed at tackling malnutrition issues in India. Marico and PepsiCo India follow by sharing second place with 5.5 points each. Among the companies that were also assessed in 2016, eight out of nine have shown improvements in their overall score in this Category. Most of this increase can be attributed to the active interest these companies have shown in support of government efforts aimed at addressing all forms of malnutrition in India. For instance, five of them clearly commit to engage with policymakers in support of such measures, and all, except for Parle Products, provide one or more examples of their efforts supporting various national initiatives.
- Although just seven companies explicitly commit to engage with the government and policymaking bodies, in support of measures designed to address all forms of malnutrition in India, 12 were able to provide examples of playing an active and/or constructive role in supporting the Indian government’s efforts in this regard. For instance, many companies have shown evidence of supporting and engaging with the food regulator to foster greater action on food safety and nutrition issues in India. This is a positive development since the 2016 Index, which indicates that the food and beverage companies are increasingly acknowledging their role in the development of public health and nutrition initiatives in India.
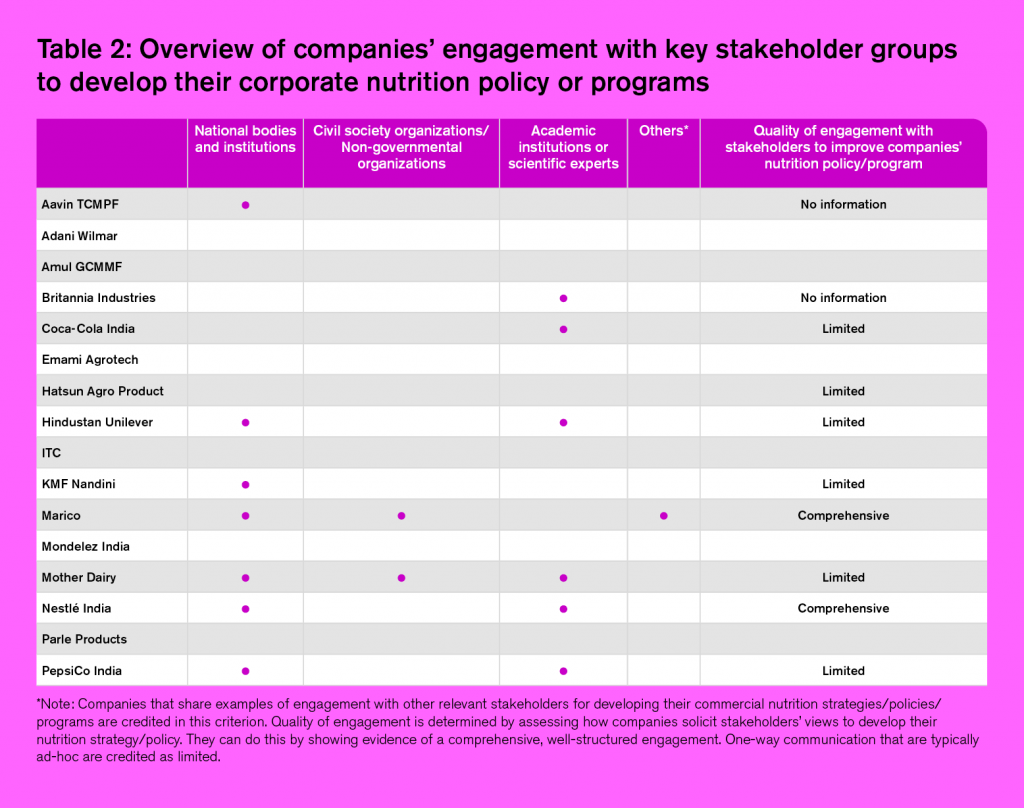
- None of the companies assessed in this Index provide any evidence of how they engaged with expert organizations and initiatives on specifically addressing malnutrition in high-risk groups. But eight indicate partnering with some organizations. ATNI found publicly available details of some of the partnerships with organizations such as Tata Trusts, UNICEF, GAIN, WFP, Save the Children and other national organizations and government bodies. Working closely with such organizations in a long-term commitment can help companies evolve their nutrition business strategies and respond better to local perspectives and needs. When it comes to consulting with stakeholders to solicit input on their corporate strategies, nutrition-related policies or activities at a broader level, 10 companies disclose some evidence. Nestlé India and Marico stand out in respect to their comprehensive, well-structured and focused engagement with Indian stakeholders around the development of their corporate nutrition strategies. Both companies have established regular interaction with stakeholders through trade associations, surveys, direct feedback and in-person meetings.
- Overall, companies’ disclosure about their interaction with stakeholders, such as industry associations, think-tanks, or other such interest groups and organizations in India, is quite limited. None of the companies achieve a full score in transparency on this subject even though nine show some degree of disclosure – mostly regarding their membership with industry associations. None disclose their financial support to influencers (individuals or groups), think tanks, interest groups or other such organizations in India. Only Coca-Cola India discloses its board seats at industry associations and on advisory bodies related to nutrition issues. Therefore, all companies assessed in this Index can improve their disclosure by being transparent about how they engage with various stakeholders.
Novelties and best practices
Nestlé India’s Council for Nutrition Affairs and other multi-stakeholder initiatives
Nestlé India aligns with its globally applied Policy on Transparent Interactions with Public Authorities 2017. The Governing Principles of such interactions include supporting public authorities in tackling societal issues such as malnutrition and diet related chronic diseases. Through this, the company commits to engage with policymakers, regulatory authorities and relevant public bodies for the development of public policies designed to address malnutrition. Nestlé India is also a member of the Confederation of Indian Industry National Committee on Nutrition, created in 2017. This National Committee works towards policy advocacy, building a consumer-connect, capacity building and knowledge creation in the area of nutrition. The Committee works in partnership with key stakeholders, such as National Institute for Transforming India (NITI Aayog), FSSAI, various ministries, NGO’s and micro, small and medium enterprises, on aligning its actions with the National Nutrition Strategy and contributing to tackling the problem of malnutrition.
In addition, Nestlé India has established an extensive engagement with internal and external stakeholders to improve its commercial nutrition strategy, and to support the development of public strategies aimed at tackling the problem of malnutrition in India. Through the Nestlé Council for Nutrition Affairs, established in 2012, the company incorporates external professionals from the field of nutrition and administration to periodically advise on its nutrition strategy and programs. Moreover, the company organizes stakeholder meetings with top-level management and external stakeholders in the field of nutrition. Nestlé India also works with stakeholders across its value chain – from farmers and suppliers to trade associations and local communities – to improve the productivity and quality of produce and to create awareness regarding water and nutrition.
Marico’s nutrition-related stakeholder engagement
Marico is the best performing India-headquartered company in this Category for its overall approach towards engaging with government bodies and stakeholders on nutrition-related issues. Marico indicates in its Annual Report 2018 that it contributes to regulatory and operational development, and other areas that affect industry and government bodies, for instance by working with FSSAI on food safety and consumer awareness. The company elaborates further in its Sustainability Report 2018 that it has engaged with FSSAI on various occasions, such as partnering with them (for 11 years) on Food Safety Training and Certification, a program that works towards capability development of government officials and working with them on school outreach programs in urban and rural areas on issues concerning nutrition and food safety (impacting more than 18,000 students).
Marico also has a well-structured approach to engaging with its various stakeholders. The Sustainability Report states that Marico engages with a broad spectrum of stakeholders, both internal and external, and with its approach rooted in principles of accountability and inclusive growth. The company further explains that it engages with each stakeholder group to work towards specific goals, one of which is related to developing its business strategy. The report goes on to present a list of key stakeholders the company has engaged with: investors, government and regulatory bodies, third party manufactures, supply chain partners, local community and NGOs. With their involvement, Marico developed a materiality matrix to identify the most important business (including nutrition issues) for the company and its stakeholders and established focus areas to set sustainability goals with measurable targets to be achieved by 2022. Some of the areas identified were in product responsibility with elements of ‘customer health and safety’ and ‘marketing and labelling’. The company further states that it has developed a vision to ensure adherence to all consumer health and safety standards and promote consumer wellbeing (mainly surrounding heart-health and nutrition awareness).
G1 Engaging and influencing governments and policymakers
- Seven companies explicitly commit to engage with the government, policymakers and policymaking bodies, in support of measures designed to address all forms of malnutrition in India (i.e. not to engage against such measures (See Table 1). Marico indicates in its annual report that it, “contributes in the development of industry and government bodies in regulatory, operational and other areas by working along with these institutions. Food safety and consumer awareness are some of the areas where Marico has participated.” (p.72) The company also goes on to highlight its work in support of FSSAI’s nutrition education and food safety initiatives.
- PepsiCo India embeds its commitment in its Health and Wellness Approach and Engagement document and states, “PepsiCo is committed to engaging in conversations with governments and other stakeholders around the world on public health topics, such as improving nutrition, addressing undernutrition, supporting responsible marketing, promoting healthy lifestyles and developing nutrition programs.” The company indicates that it participates in public policy dialogue with government officials and other stakeholders where they can share their expertise and contribute ideas to solve policy issues.
- Among the 12 companies that have provided examples of playing an active/constructive role, nine have shared multiple examples of positive engagement with government initiatives and programs. These include engaging with FSSAI’s Eat Right Movement; taking voluntary steps to not promote/sell foods that are high in fat, salt and sugar (HFSS) in schools (according to FSSAI’s ‘Safe Food and balanced diet for Children in School’ regulation that bans such foods in school canteens); support national/state level initiatives, such as the Integrated Child Development Services, National Mid-day Meal Scheme, etc.; and/or other similar initiatives. Coca-Cola India, Mondelez India and Nestlé India provide most examples by showing evidence of support towards each of these initiatives. For instance, all three companies have strict responsible marketing policies that commit to not marketing or selling any of their products in schools, indicating their support to FSSAI’s ‘Safe Food and balanced diet for Children in School’ regulations. The remaining three companies have shared one example per company, indicating that there is ad-hoc engagement around these types of initiatives related to nutrition.
- Most companies disclose limited information about their interactions with their key stakeholders, some of which engage on their behalf at the public policy level in India. Thus, none of the companies get a full score in this area. Nine companies limit their disclosure to their membership with industry associations. In 2016, only Nestlé India and Hindustan Unilever were found to disclose the details of their membership in the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (FICCI). In this 2020 Index, Britannia Industries, Coca-Cola India and PepsiCo India were also found to have published information about their memberships and engagement with such organizations. For instance, PepsiCo India indicated that the details of its membership in organizations such as CII, FICCI, ASSOCHAM, AFSTI, FBAI and IBA are publicly disclosed. Britannia Industries published in its Annual Report 2018 (annex Business Responsibility Report), that “working together with the institutions or associations engaged in policy advocacy like Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India etc., will help the Company create positive social and environment impact while achieving its business goals. The Company’s approach to deal with these institutions is guided by the principles of the Code of Business Conduct i.e. honesty, transparency, integrity and accountability.”
- Among companies assessed in this 2020 Index for the first time, Adani Wilmar, ITC and Marico disclose evidence of their membership to industry associations or other organizations that lobby on its behalf. In its Business Responsibility Report (an annex to its Growth with Goodness Annual Report 2017-18), Adani Wilmar states that it is a member of CII, Independent Power Producers Association of India, Gujarat Chamber of Commerce and Industry and FICCI. The company also states that it has advocated on food security with respect to edible oil and pulses but does not describe the details of this process.
- None of the companies assessed in this Index disclose their financial support to industry associations, influencers (individuals or groups), think tanks, interest groups or other such organizations in India. This is similar to the findings of the 2016 Index.
- Coca-Cola India not only publishes the names of the stakeholder groups it is a member of but also discloses its board seats at industry associations and on advisory bodies related to nutrition issues. The company discloses this information in its Sustainability Report (Sustainability Update 2017/18 Supplementary Report, link on p.14) with a list of 15 organizations and Coca-Cola India’s association with some of them. For example, it is on the management committees of the Indian Beverage Association and Pet Packaging Association for Clean Environment.
To increase transparency and positively engage with government and policymakers to impact consumers’ access to nutrition, food and beverage manufacturers in India are encouraged to:
- Commit to engage with the Indian government and policymakers in support of measures designed to address all forms of malnutrition such as FSSAI’s Eat Right India campaign, Poshan Abhiyaan, etc. i.e., to not engage against such public health measures.
- Increase transparency around membership of industry associations, such as Confederation of Indian Industry, FICCI, think tanks, or interest groups. Similarly, companies should publicly disclose financial support to these organizations, including board seats at industry associations, advisory bodies related to nutrition issues and potential governance conflicts of interest.
- Disclose their policy positions and advocacy goals on key nutrition issues in India.
G2 Stakeholder engagement and partnerships
- 10 companies provide evidence of engaging with stakeholders in developing their commercial nutrition strategies. The stakeholders were categorized into five groups: national bodies and institutions; civil society organizations/non-governmental organizations (CSO/NGOs), academic institutions or scientific experts and/or other relevant stakeholders the company consulted with (See Table 2). Marico and Mother Dairy provide evidence of consulting with the greatest number of stakeholders. In its Sustainability Report 2018, Marico provided a list of key external stakeholders (investors, government and regulatory bodies, third party manufacturers, supply chain partners, local community and NGOs) it engages with, in order to conduct materiality assessments through which it informs its efforts in research and development, product quality and safety, consumer wellbeing, and marketing and labelling.
- Nestlé India is best in the class when it comes to seeking specialist external expertise to design its commercial strategy, addressing both obesity and diet-related chronic diseases, and undernutrition or micronutrient deficiencies (at the board level). The company has organized its engagement through an advisory committee – Nestlé Council for Nutrition Advisory. Coca-Cola India also shows evidence of organizing its engagement into an advisory panel or expert group that meets regularly to form its Health & Wellness Advisory Council of Science. The Council guides the company to identify the evolving nutritional needs of Indian consumers and suggest viable locally relevant solutions for beverage applications. The Council also helps guide the company on strategic projects in line with new developments and trends in India.
- Eight companies indicate that they have partnerships with or formally support key national initiatives/organizations to address malnutrition among groups at high-risk. Some of the organizations that the companies indicate partnering with are Tata Trusts, GAIN, WFP, Save the Children and Narayana Health. Disclosure by the companies around the partnerships and related activities, as well as outcomes, were also found to be limited.
- KMF Nandini describes its collaboration with the National Dairy Development Board and Tata Trusts to take steps towards fortification of its Nandini toned milk, double toned milk, special toned milk and standardized milk with vitamins A and D. Britannia Industries, through its Britannia Nutrition Foundation, collaborates with Narayana Health, National Health Mission, Rajasthan and the Jaipur education department on the SUPOSHAN program. This program is designed as an action research study aimed at introducing iron fortification in a palatable manner, which would be an adjunct to the existing Weekly Iron Folic Acid Supplementation program in India.
To improve and accelerate their engagement with stakeholders in order to impact consumers’ access to nutrition, food and beverage manufacturers in India are encouraged to:
- Conduct comprehensive, well-structured engagement with relevant stakeholders in India with the aim of improving their business strategy and performance relating to nutrition, as well as when developing new nutrition-related policies, setting new targets or developing new initiatives and programs.
- Engage systematically and/or establish formal, long-term partnerships and one-on-one discussions with credible international/local organizations, CSOs/NGOs, academic institutions and scientific experts, and other such organizations actively working towards addressing all forms of malnutrition in India in high-risk groups and to evolve companies’ commercial approach.
- Disclose examples of engagement with key organizations and how their input has been used in developing the companies’ policies, strategies or programs and what the outcomes are.