India Index 2023
The Access to Nutrition Initiative (ATNI) is pleased to present the India Index 2023. This Index assesses the performance of 20 of the largest Indian food & beverage manufacturers which together comprise an estimated 36% of total sales of packaged foods & beverages in the country.
Introduction
The India Index 2023 shows the current state of play of food & beverage companies' contributions to diets and the food environment in India.
The influence of the food & beverage industry is growing. It has both the responsibility and the opportunity to embed nutrition into its core business, improving product offerings for consumers. Actioning the Index recommendations will facilitate food & beverage manufacturers to play a more vital part in addressing pressing nutrition-related concerns and ensuring that a healthy, affordable diet is available to all. ATNI and its partners hope that the India Index 2023 provides useful data and analyses that support companies, investors, civil society and policymakers to make informed steps towards improving nutrition in India.
Sales of packaged food and beverages in India have surged by 15% year-on-year since 2011, outperforming total sales of food. Meanwhile sales of highly processed foods typically high in fat, salt or sugar (HFSS) are projected to double by 2030. Amid these trends, India is witnessing its highest levels of micronutrient deficiencies and obesity.
ATNI’s analysis of the healthiness of 20 of the country’s largest F&B manufacturers’ products shows there have been incremental improvements since its first analysis in 2016. These trends stress the urgency, opportunity and responsibility for food companies, investors and public health and food authorities in India to ensure processed packaged foods meet healthiness standards. Doing so would enable consumers to follow dietary guidelines and eat better while simultaneously preventing millions of cases of obesity and micronutrient deficiency.
ATNI was established in 2013 to transform markets for nutrition and measure and drive forward private sector accountability. ATNI assessed the largest food & beverage manufacturers in India in both 2016 and 2020 on their contribution to healthier diets for all Indians.
The India Index 2023 can be used by a range of different stakeholders to drive progress including:
- Companies and industry associations to show how their practices can be improved, compare with their peers, and incentivize progress
- Responsible investors as a tool for decision-making on investing in and engaging with companies
- Policymakers to help identify priority areas for regulation and government-led action
- Civil society as an evidence-base for engagement with industry as well as with consumers.
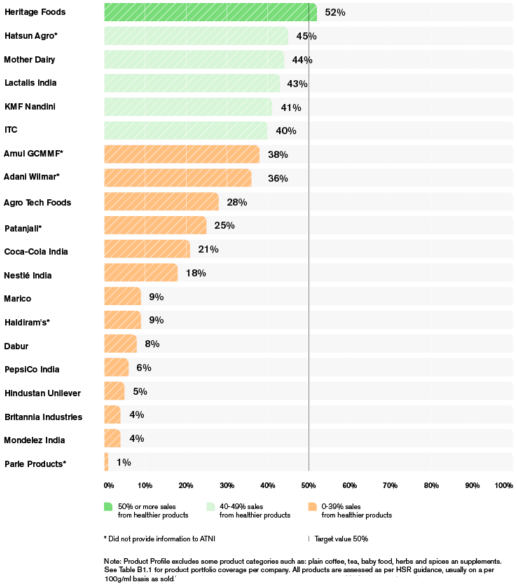
Product Profile
The India Index 2023 Product Profile assessment found that 76% of sales were derived from less healthy products.
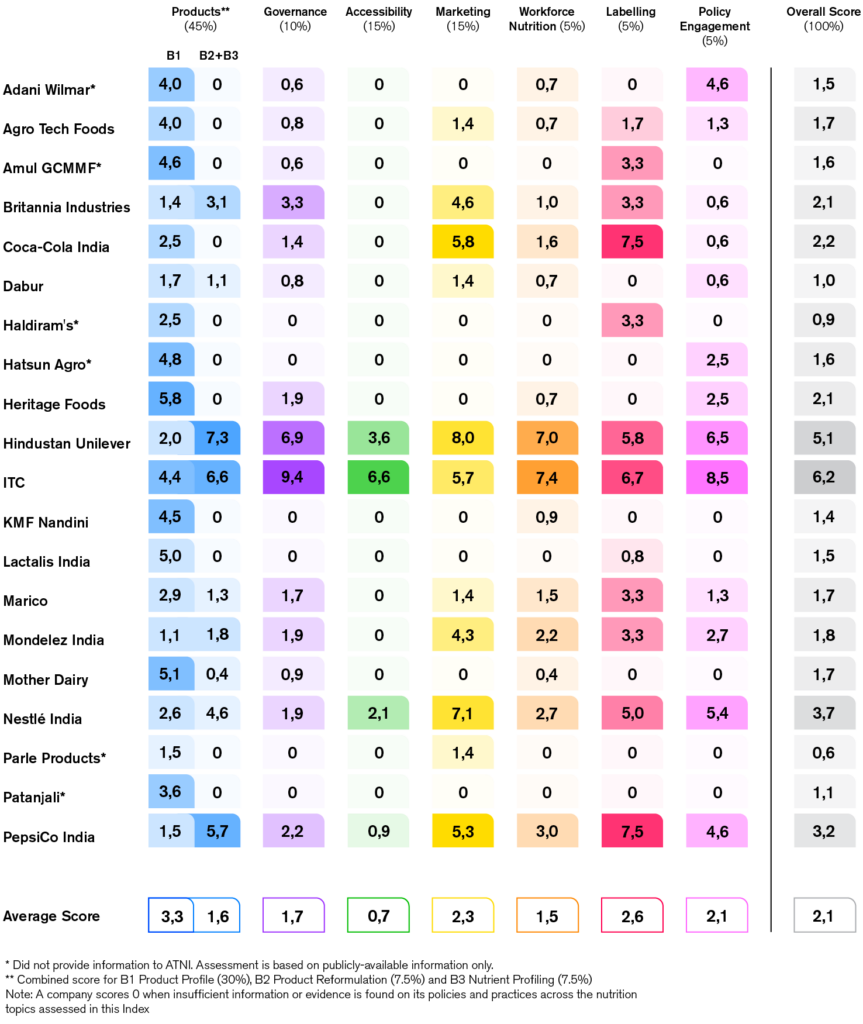
Overall Scores
There is considerable variation in the performance of companies across different nutrition topics.
Key Findings
Food & beverage companies have a significant opportunity to improve their nutrition policies and practices in India.
Based on 1,901 products analysed from the 20 indexed companies, 76% of sales are derived from less healthy products. The mean healthiness of companies’ products was found to be 1.9 stars out of 5.0, with substantial variation observed between companies.
Companies continue to publicly acknowledge the need to improve the healthiness of their products and their role in consumers’ diets. However, this recognition is not always translated into clear definitions coupled with ambitious targets and action required to drive meaningful progress.


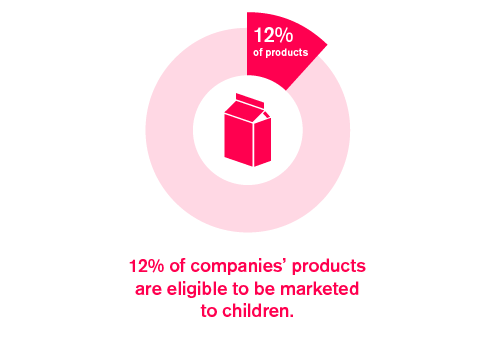
Seven companies were found to have a publicly available responsible marketing to children policy in India. When using WHO SEAR criteria, 12% of all products assessed were found to be eligible to be marketed to children.
Five companies showed evidence of having clearly defined workforce nutrition programs in place, of which two companies include measurable targets.

Four companies showed evidence of having a formal affordability approach or strategy to making ‘healthier’ foods (according to the company’s definition of healthy) more available coupled with a definition of ‘lower-income consumers’ in India. However, apart from one company, transparency regarding these initiatives was limited, none had disclosed targets, and evidence of implementation was unclear.
Six companies provide nutritional information on front of pack (FOP) in a numerical format for key nutrients. Companies are waiting for a decision on the proposed Indian Nutrition Rating (INR) FOP labelling system before introducing any new FOP labelling, to avoid confusing consumers and potentially wasting resources changing packaging designs.
Seven companies out of 20 were found to have a responsible advocacy policy in place in India, although in most cases these articulated only high-level principles. Twelve companies disclose comprehensive lists of trade association memberships in India, four of which also indicating the associations in which they hold Board seats (or equivalent).
Reductions of scope 1, 2, and especially 3 emissions – along with food loss waste (FLW) — are generally not yet reported by Indian food companies. Plastic use reduction and transitioning to sustainable forms of packaging appears to be the most frequent sustainability action for companies, with almost all companies demonstrating evidence of targets or activities in this space. This likely reflects the need for companies to comply with Indian plastic waste regulations.
Key Recommendations
To better support nutrition outcomes in India, it is recommended that food systems actors consider taking the following actions:
Food & beverage companies:
Companies can improve their product portfolios leading to at least half of their portfolio (sales and products) meeting healthy thresholds by 2030 by:
- Adopting specific, measurable, and timebound targets to reduce nutrients of concern and increase positive ingredients across their portfolio in India.
- Using an (inter-)nationally recognized NPM to measure, define and report on the healthiness of products in their portfolio.
- Publicly disclosing on an annual basis the percentage of their product portfolio that meets these healthiness criteria.
Companies are encouraged to fully integrate nutrition considerations into their commercial business functions by:
- Assigning formal responsibility for the success of their nutrition strategy to the highest levels of seniority within the company in India
- Developing specific strategies to increase sales of ‘healthier’ products relative to unhealthy products, through pricing, distribution, and marketing investments.
- Setting and reporting against a target to increase sales of products defined as ‘healthier’ relative to overall sales.
- Adopt and publish an affordability strategy to deliver more affordable, and accessible products and improve lower-income consumers’ diets in India.
- Develop and publish a comprehensive responsible marketing policy that covers all media channels and audiences, including for children under the age of 18.
- Ensure they develop workforce nutrition programs, including healthy food at work, nutrition education, nutrition-related health check-ups and breastfeeding support with meaningful and quantifiable outcomes.
- Adopt and publish a comprehensive nutrition labelling policy in alignment with recent regulations including front-of-pack information, back-of-pack information and how label information is comprehensively addressed online.
- Adopt a responsible advocacy policy that extends to cover any third parties advocating on behalf of the company. It should include commitments to conduct themselves responsibly; be transparent about their identity and intentions; only present valid, independent, and representative evidence; and consider the wider public interest and public health in their efforts.
Investors:
As shareholders, investors play a significant role in shaping food companies’ governance, strategy and disclosure practices.
- First, investors can make use of existing nutrition frameworks such as ATNI’s Investor Expectations on Nutrition, Diets and Health using this to integrate nutrition into responsible investment strategies.
- Second, investors can use the findings of this Index to drive companies’ progress on nutrition in India through various investment strategies, calling for transparency and standardization of companies’ reporting across nutrition metrics.
Read more about ATNI’s work with investors
Policy Makers:
- First, a transparent definition of processed foods and and NPM would help align the sector.
- Second, global evidence on the effectiveness of fiscal incentives and health tax models is growing and could be deployed in India.
- Third, clear and transparent labelling guidelines that incorporate the definition of highly processed foods and FOP labelling should be established. Effective monitoring of these labelling guidelines should also be established to ensure compliance.
- Lastly, environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing policies should integrate nutrition where appropriate.
Report Chapters
Click on the tiles below for detailed findings across the seven nutrition topics assessed in this Index.
Download Full Report
Download Executive Summary
Download Chapter
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Download Category Report
Company Scorecards
Click on the tiles below for a detailed overview of individual companies' performance and key recommendations.

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard
Go to company scorecard

Go to company scorecard
Methodology
This Index includes a Corporate Profile and Product Profile assessment, which together assess companies nutrition policies and practices, and the healthiness of their portfolios in India.
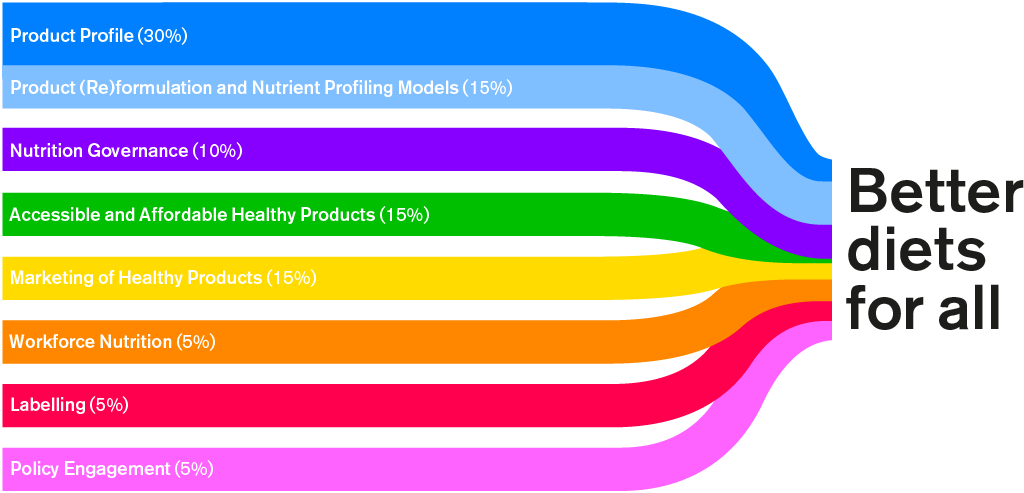
The Index methodology deploys 58 indicators across seven categories on which companies are scored. Each category is weighted according to the relative impact it is considered to have on diets of consumers across India, building on evidence generated from ATNI’s 10-year Index experience.
For this Index, ATNI placed a greater focus on assessing nutritional quality of products in companies’ portfolios, formal targets, strategies, and policies, rather than broad commitments and general statements.
Amplifying Impact
ATNI encourages all stakeholders to actively use the India Index results and provide their feedback to ATNI. We hope that the rated companies will commit to make changes based on our recommendations and that their investors will use them in their engagement with those companies to press for improvements in their policies, practices and disclosure. Further, we hope that governments and policymakers, NGOs, academics and others are able to use our analysis and findings in their work to encourage better diets in India.
ATNI aims to drive food systems transformation through driving food & beverage companies’ progress over time. Take a look at our Trends Over Time tool.
Acknowledgements & Disclaimers
The India Index 2023 is being supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO). This report was produced by the India Index team, consisting of: Babs Ates, Bo-Jane Woods, Brenda de Kok, Elena Schmider, Freddie von Kaufman, Greg S. Garrett, Mark Wijne, and Will Sharp. The ATNI team drew on the expertise and advice of the ATNI India Index Expert Group (N. Arlappa, Meetu Kapur, Tarun Vij, and Dr. Rajan Sanka), ATNI consultant Vivek Arora’s close engagement throughout the ATNI development process has been a source of invaluable guidance. This report benefited greatly from his input. The views expressed in this report, however, do not necessarily reflect the views of the group’s members or their institution. ATNI would also like to thank our partners Dr. Elizabeth Dunford from The George Institute for Global Health for research, Kummer & Herman and Studio September for design, Wren Media for editing, 73Bit for setting up the data platform and Kaizzen for communications.
Without limiting any of the foregoing and to the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event shall Access to Nutrition Foundation, nor any of its respective affiliates, The George Institute, Euromonitor International, Innova Market Insights, or contributors to or collaborators on the Index, have any liability regarding any of the Information contained in this report for any direct, indirect, special, punitive, consequential (including lost profits) or any other damages even if notified of the possibility of such damages. The foregoing shall not exclude or limit any liability that may not by applicable law be excluded or limited.

Download Pdf
Access an overview of the major findings and recommendations of the India Index 2023.